Ceramic dental implants, made from zirconia, are gaining popularity as an alternative to titanium implants. Are they the better choice for you? This article will explain what ceramic dental implants are, their benefits, and potential drawbacks, so you can decide with confidence. Ceramic is sometimes called the holistic dental implant.
Contact us for a no cost ceramic implant consultation.
Key Takeaways
- Ceramic dental implants, made from zirconia, are a metal-free alternative to titanium implants and offer advantages like reduced allergic reactions, biocompatibility, and esthetic benefits.
- Ceramic implants come in one-piece and two-piece designs, with one-piece implants minimizing bacterial leakage and two-piece designs providing greater restorative flexibility.
- While ceramic implants are more aesthetically pleasing and suitable for patients with metal sensitivities, they are generally more expensive and require precise surgical techniques due to their brittleness.
Understanding Ceramic Dental Implants
Dental implants are designed to replace the root of missing teeth, preserving the bone and providing a stable foundation for tooth replacement. The choice of implant material is paramount, influenced by the patient’s needs and personal preferences. While titanium dental implants have been the gold standard for decades, ceramic implants are emerging as a viable alternative.
Ceramic implants, made predominantly from zirconia, offer several advantages over traditional metal implants, including zirconia and titanium implants. Zirconia dental implants resolve issues commonly associated with titanium implants, such as allergic reactions and metal sensitivities. By focusing on patient health and safety, practitioners aim to provide the best possible outcomes for dental implant patients.
Characteristics of Ceramic Dental Implants
Ceramic dental implants are crafted from zirconia, a metal-free material known for its strength and biocompatibility. These implants come in both one-piece and two-piece configurations, each with its unique set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for both dental professionals and patients when considering dental implant options.
One-piece ceramic implants are favored for their simplicity and reduced risk of bacterial leakage, while two-piece designs offer restorative flexibility. The diameter of ceramic implants ranges from 3.3 mm to 7 mm, accommodating various clinical needs and patient preferences.
Ceramic implants are a central part of tooth replacement for a biological and holistic dental practice.
Material Composition
Ceramic implants are primarily made of zirconia, produced through sintering or yttrium-stabilized processes. This strong, white material is chosen for its beneficial properties in dental prosthesis, offering a metal-free alternative that is both durable and aesthetically pleasing.
Design and Structure
Ceramic implants are available in one-piece and two-piece designs. One-piece implants, fused into a single monobloc, minimize bacterial leakage and are preferred for their simplicity.
Two-piece designs, similar to advanced titanium implants, consist of an implant body, abutment, and retention screw, providing greater restorative flexibility but with a potential risk of bacterial leakage at the joint. These characteristics are common in titanium implant systems.
Clinical Benefits of Ceramic Dental Implants
Ceramic dental implants offer numerous clinical benefits, making them an appealing choice for many patients. Their biocompatibility, esthetic advantages, and metal-free composition contribute to their growing popularity in implant dentistry, including the use of clin oral implants.
One of the key benefits of ceramic implants is their reduced bacterial attraction compared to titanium implants, which lowers the risk of gum disease. Additionally, their resistance to chemical corrosion and lack of electrical conductivity make them a stable and safe option for dental implants.
07ca9081 1278 4ff3 89a3 db6be267845f 1
Biocompatibility
Ceramic implants are hypoallergenic and biologically compatible, promoting healthy osseointegration with the jawbone. Their bioinert nature reduces the risk of implant site complications and inflammation in surrounding tissues.
Furthermore, their low affinity for plaque aids in maintaining peri-implant health.
Esthetic Advantages
Ceramic implants offer excellent esthetics, closely resembling natural tooth enamel and blending seamlessly with natural teeth. They are particularly beneficial for patients with thin or translucent gums, as they prevent gum discoloration, unlike titanium implants which can cause a grayish appearance.
Metal-Free Option
For patients seeking a metal-free solution, ceramic dental implants are ideal. Made from zirconium oxide, they are hypoallergenic and do not cause allergic reactions, making them suitable for patients with metal sensitivities or those who prefer to avoid metal dental implants.
This metal-free option aligns with holistic health principles and is increasingly preferred by patients with allergies to metal.
Surgical Considerations for Ceramic Implants
The surgical placement of ceramic dental implants requires a higher level of skill compared to titanium implants. Proper technique and precision are crucial to ensure successful outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Two-piece ceramic implants often include a retention screw made from various materials, such as titanium, gold, carbon, or zirconia, which necessitates precise torque application during placement. This highlights the importance of experienced dental professionals in handling ceramic implants.
Placement Techniques
The placement of ceramic implants involves specific surgical techniques, such as low drilling speeds to prevent overheating and bone loss. One-piece implants can be placed using a flapless approach, though this may result in more bone loss.
Initial guided surgery can help ensure correct positioning, and delayed or late loading is often recommended to address primary stability issues.
Healing and Integration
Healing and integration for ceramic implants typically require several months, similar to titanium implants. Both types involve initial discomfort for about a week, followed by a longer period for the implant to anchor to the jawbone. Despite the time required, both ceramic and titanium implants show no significant differences in the healing process.
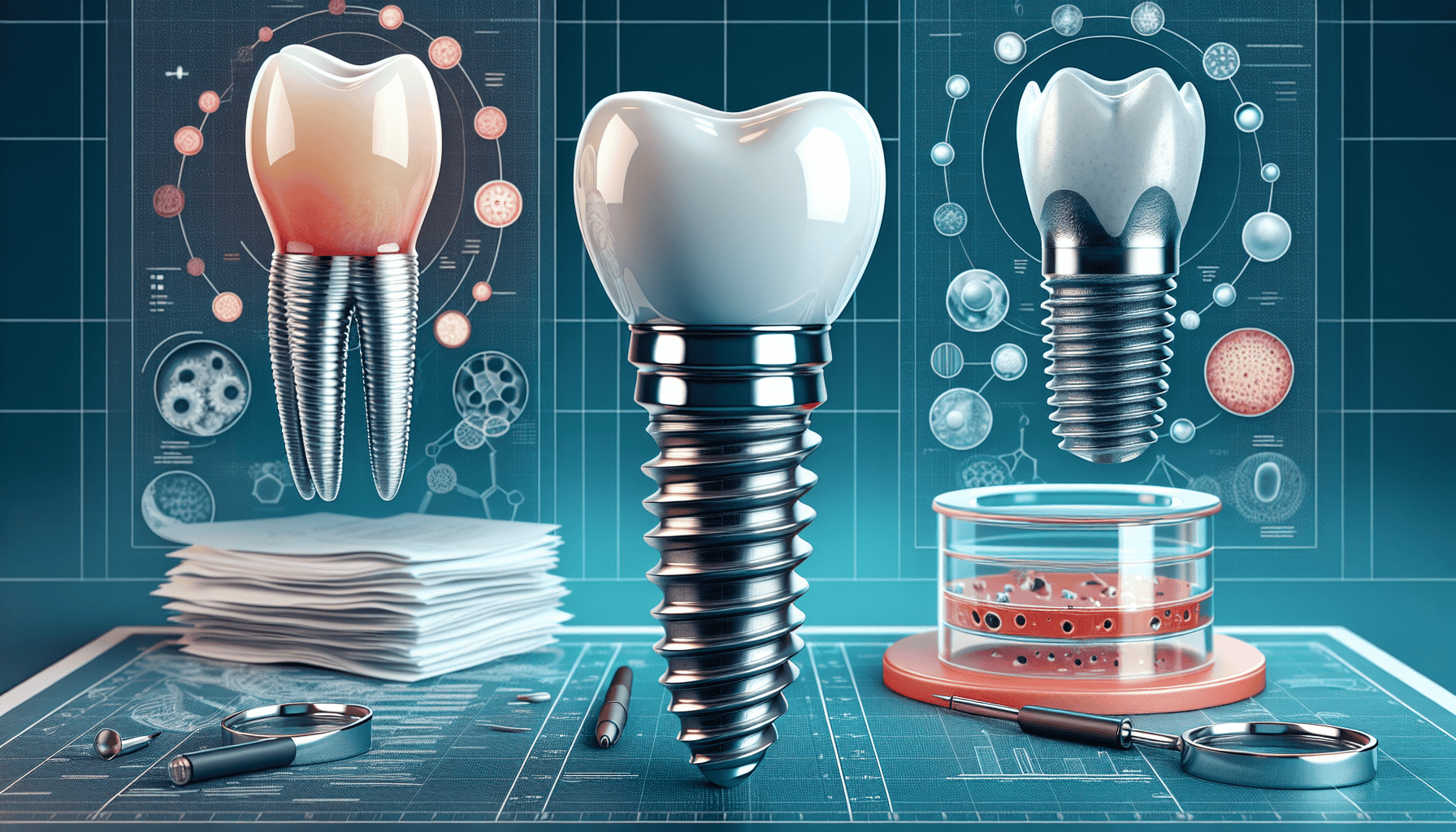
Comparing Ceramic and Titanium Implants
Ceramic and titanium dental implants each have distinct advantages and considerations. While ceramic implants offer excellent esthetics and reduced risk of allergic reactions, titanium implants are known for their robustness and long-term success.
Titanium implants generally cost about $300 less than ceramic implants, which can be a deciding factor for some patients. Understanding these differences helps patients make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
a439521e 0820 49dc 8e5b d5c044dca4f7
Strength and Durability
Modern ceramic implants exhibit high compression and flexural strength. However, they can be more brittle than titanium implants, making them prone to fractures under certain conditions.
On the other hand, a titanium implant boasts excellent tensile strength and resistance to external forces, rarely experiencing implant fractures in the case of titanium implants.
Cost Differences
Ceramic dental implants are generally more expensive than their titanium counterparts due to their material and production processes. The higher manufacturing cost of zirconia implants contributes to this price difference, making them less accessible for some patients.
Clinical Research and Longevity
Titanium implants have a long history of scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness, with a 10-year success rate of 97%. While ceramic implants show similar integration capabilities, titanium may demonstrate faster initial osseointegration. Both types are effective and reliable, with titanium having a longer documented success history.
Patient Perspectives and Preferences
Patients often have specific preferences when it comes to dental implants, including mini dental implants, influenced by holistic health principles, aesthetic concerns, and comfort and functionality.
Many patients with a holistic approach to dental care prefer ceramic implants due to their biocompatibility and absence of metal, aligning with their health and wellness philosophies. Additionally, ceramic implants are favored for their natural tooth-like appearance, making them particularly appealing for patients who prioritize esthetic outcomes.
Holistic Approach
Patients with holistic health principles often choose ceramic implants because:
- They are metal-free and biocompatible
- They do not interfere with the body’s natural functions
- They are less likely to cause immune responses or allergic reactions.
Aesthetic Concerns
Ceramic implants are perceived to have better aesthetic outcomes compared to metallic implants. They blend seamlessly with natural teeth, especially in esthetic areas, ensuring a more natural look for patients.
Comfort and Functionality
Patients report that ceramic implants offer several benefits, including:
- Feeling more comfortable and natural in the mouth
- Improving overall satisfaction with the implant
- Functioning comparably to natural teeth in daily use
- Contributing to positive long-term experiences
Addressing Common Concerns
While ceramic dental implants offer numerous benefits, there are common concerns related to potential implant failure and allergic reactions. Addressing these concerns is crucial for both patients and dental professionals.
Ceramic implants have a specific incidence of failure comparable to titanium implants, influenced by factors such as surgical technique and patient health. Early studies suggest that the risk of ceramic implant failure may be slightly higher due to the material’s brittleness, but advancements in design are addressing these concerns.
Potential for Implant Failure
The placement of ceramic implants can be more technique-sensitive than metal implants. Factors such as implant length, diameter, and bone quality significantly influence implant success. Systemic conditions like smoking and diabetes are critical risk factors for implant failure.
Infection at the implant site is also a common risk factor for failure, including for ceramic implants.
Managing Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to dental implant materials are relatively rare but can manifest as localized swelling or discomfort. Patch testing and the MELISA test can help identify potential allergies to implant materials before the procedure. In case of an allergic reaction, removing the implant and replacing it with an alternative material may be necessary.
Choosing the Right Implant for You
Selecting the most suitable dental implant material depends on individual needs and preferences. Ceramic implants should be handled by dentists who specialize in dental surgeries due to their specific requirements. Patients with a thin or delicate soft tissue biotype may prefer ceramic implants because of their white color and aesthetic advantages.
Ceramic implants are ideal for patients who:
- Prefer a 100% metal-free material
- Have known metal allergies or sensitivities
- Are concerned about potential visibility, especially in the anterior region where aesthetics are crucial.
This option is particularly suitable for these patients.
Ultimately, the decision between ceramic and titanium implants should involve a thorough discussion with your dental professional, considering factors such as:
- biocompatibility
- esthetics
- cost
- personal health history
By evaluating these aspects, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your dental and overall health goals.
Summary
Ceramic dental implants offer a compelling alternative to traditional titanium implants, with benefits such as excellent esthetics, biocompatibility, and a metal-free composition. They are especially suitable for patients with allergies to metals or those who prioritize a holistic approach to their health. However, it’s essential to consider factors such as cost, potential for implant failure, and the specific skills required for their placement.
In conclusion, both ceramic and titanium dental implants have their unique advantages and drawbacks. By understanding these differences and consulting with a qualified dental professional, patients can make an informed decision that best meets their needs. Whether you opt for the aesthetic appeal of ceramic or the long-standing reliability of titanium, the ultimate goal is to restore missing teeth and achieve a healthy, functional, and beautiful smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ceramic dental implants offer excellent esthetics, biocompatibility, and a metal-free composition, making them suitable for patients with metal allergies or those who prioritize a natural look. They also provide a strong and durable alternative to traditional implants without compromising on appearance.
Ceramic implants have high compression and flexural strength, but they can be more brittle than titanium implants, which are known for their tensile strength and resistance to external forces. Therefore, in terms of strength and durability, titanium implants are generally more robust than ceramic implants.
Yes, ceramic dental implants are generally more expensive than titanium implants due to their materials and production processes. This higher cost can limit accessibility for some patients.
When placing ceramic dental implants, it’s important to use specific techniques like low drilling speeds to prevent overheating. Precision is crucial for successful outcomes.
Yes, ceramic implants can fail due to factors like poor osseointegration and mechanical stress. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to ensure proper surgical technique, consider patient health factors, and use experienced dental professionals.

 (301) 421 1996
(301) 421 1996 burtonsvillesmiles@gmail.com
burtonsvillesmiles@gmail.com